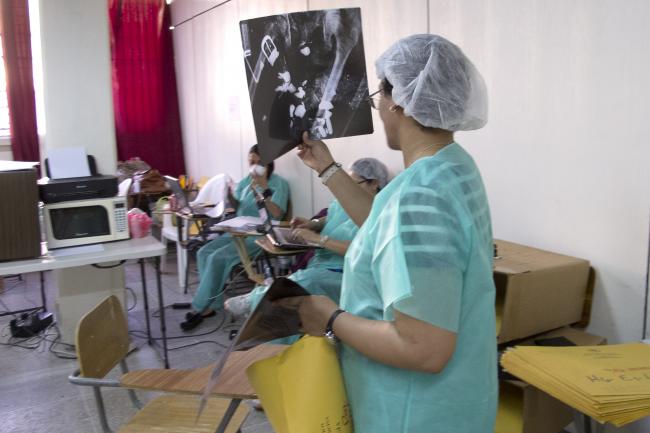
Forensic anthropology in crisis settings: a required component of investigation in the world‘s trouble spots
This article presents an account of the involvement of forensic anthropology in the investigation of human rights abuses in the modern era, and the difficulties it faces with respect to lack of adequate funding, volatile settings, the presence of unexploded ordnance, corruption in governmental agencies and a lack of good will, absence of support for NGOs and the curtailment of formal judicial proceedings to effect transitional justice. Syria, Iraq, Afghanistan, Spain, Mexico and the Northern Triangle are provided as regional examples of the problems encountered when attempting to conduct forensic anthropological investigations to locate mass graves, retrieve victims and obtain proper identifications. Interventions by various organisations are highlighted to illustrate their assistance to forensic and non-forensic individuals through technical support, training and mentoring in the areas of crime-scene management and identification techniques. Interventions in mass-grave processing when state agencies have failed, the importance of DNA banks and information from family members and witnesses are also presented.